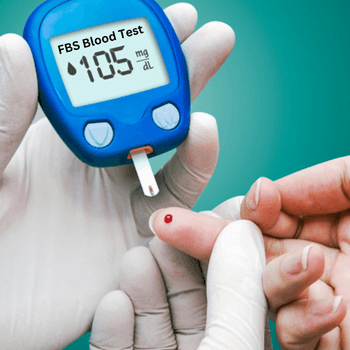
Pre – requisite : Overnight fasting (10-12 hrs) is required. Do not eat or drink anything except water before the test.
What is a Fasting Blood Sugar (FBS) Test?
The Fasting Blood Sugar (FBS) test measures the blood glucose/sugar levels in a blood sample following a fasting period of 8 hours . The FBS is a fundamental test for the diagnosis and monitoring of prediabetes and diabetes. Diabetes is a condition associated with consistently elevated blood sugar levels due to the insufficient production or ineffective use of insulin hormone by the body. Prediabetes is a stage before diabetes, also known as borderline diabetes, where the blood sugar levels are slightly elevated but not high enough to be diagnosed as diabetes. The test is also done to check for gestational diabetes – diabetes that occurs in pregnant women due to the effect of pregnancy hormones.
The FBS test provides a precise evaluation of how effectively the body regulates blood glucose levels in the absence of recent food intake. The test helps to evaluate and manage impaired glucose metabolism and diabetes in a person.
Fasting Blood Sugar (FBS) Test Parameters
Glucose, commonly referred to as blood sugar, is the main sugar present in the blood. The parameter measured in an FBS test is the blood sugar in a fasting state when the baseline sugar levels are most accurate.
Elevated blood sugar levels can be a result of several factors, such as unhealthy dietary habits, sedentary lifestyle, obesity or excess body weight, and a family history of diabetes.
Glucose is obtained from carbohydrates in the diet. During digestion, these carbohydrates are broken down and glucose is released into the bloodstream. Insulin – a hormone produced by the pancreas – enables the entry of glucose from the blood into the body’s cells where it is used for energy. As the cells absorb glucose, blood glucose levels decrease. Thus, sugar levels in the blood remain controlled. However, in an individual with diabetes, the pancreas does not make enough insulin or the body does not respond to insulin effectively, resulting in consistently elevated blood sugar levels. Over time, elevated sugar levels can damage the blood vessels and nerves and lead to serious health problems.
Fasting Blood Sugar (FBS) Test Preparation
Preparing for an FBS test requires adherence to specific guidelines to ensure accurate results. They are as stated below:
Prerequisites
It is imperative to not consume any food or drink, except water, for a minimum of 10-12 hours before the FBS test. Since food affects sugar levels, testing in a fasting state gives a more accurate picture of blood sugar levels.
The best time to get tested
The FBS test is usually scheduled in the morning before breakfast. This timing ensures that the individual has undergone overnight fasting for accurate test results.
Who can do the FBS test
Individuals with symptoms of diabetes (such as increased thirst, frequent urination, unexplained weight loss, and increased hunger) or who have risk factors for diabetes such as obesity or a family history of diabetes are eligible for the FBS test. Besides being a screening test to check for diabetes, the FBS test is done along with Postprandial Blood Sugar (PPBS) to monitor treatment efficacy in individuals with diabetes. The test is also done as part of routine health assessments to monitor blood glucose levels and to check for gestational diabetes in pregnant women.
Cautions before taking the FBS test
Before undergoing the FBS test, it is essential to inform your healthcare provider about any medications you have been taking. Certain medications can potentially influence blood sugar levels, thereby affecting the accuracy of the test results.
Fasting Blood Sugar (FBS) Test Results & Interpretation
The results of the FBS test can be interpreted as per the table below:
| Fasting Blood Sugar Level Normal Range | Interpretation |
|---|---|
| 70 – 99 mg/dL | Normal fasting blood sugar level |
| 100 – 125 mg/dL | Indicates prediabetes; blood sugar levels are higher than normal but not high enough to classify as diabetes |
| 126 mg/dL or above, on more than one occasion | Indicates high blood sugar, the main sign of diabetes |
Interpretation of Abnormal Results
Low blood glucose levels, when blood sugar levels fall below 70mg/dL, may be due to an overdose of insulin, insulinomas (tumours in the pancreas that produce insulin), starvation, adrenal insufficiency, (underactive adrenal glands), drinking excessive alcohol, severe liver disease, hypopituitarism (underactive pituitary function), hypothyroidism (low thyroid function), and severe infections.
High blood glucose levels most frequently indicate diabetes, but many other diseases and conditions can also cause elevated blood glucose, such as acromegaly (excess growth hormone), acute stress (response to trauma, heart attack, and stroke for instance), Cushing syndrome (excess cortisol hormone), hyperthyroidism (increased thyroid function), pancreatic cancer, and pancreatitis (inflammation of pancreas).